Disclaimer: As a brokerage, BitOasis routes your buy and sell transaction orders to our liquidity providers. As such we do not have our own order book where we match buyers with sellers. The information below is the order book of one of our liquidity provider partners. More details.
Definition of a Market
A market is a place where buyers and sellers exchange goods or services with each other. BitOasis Pro is just that – a place that connects buyers and sellers who want to exchange FIAT (AED) and 12 types of digital assets. We do this through an orderbook.
Orderbook?

In order for you to trade digital assets on BitOasis Pro, you need to sign up for a verified account. We do this to ensure all our customers are vetted so they can transact securely on BitOasis. Once you have a verified account, you gain access to our orderbook, through which you can enter orders.
Once BitOasis receives an order from you, the order is transmitted to the orderbook, where your order will be separated into bids (buys), and asks (sells) for immediate execution, or execution at a point you set in case of Limit, Stop and Stop-Limit Orders (for more information on the different types of orders, please see the example below).
In the figure above, you can see the bids on the left of the orderbook, and the asks on the right. By looking at the highest bid, also called the market bid or best bid, and the lowest ask, also called the market ask or best ask, you get an indication of the market rate.
The difference between the best bid and best ask is called the bid-ask spread, which can tell you how efficient and active a market is. A high or wide bid-ask spread shows that the bid and ask prices are far apart and might indicate that the buyers and sellers willing to trade are fewer generally. A low or narrow bid-ask spread shows that the bid and ask prices are quite close together and might indicate that there are more buyers and sellers willing to trade.
What are Trades?
Trades take place when bids and asks are confirmed; also known as executions, trades are considered complete, or an executed order, when abid or an ask finds a counterpart.
BitOasis Pro allows you to look up every trade that took place in the past under the Trade History tab.
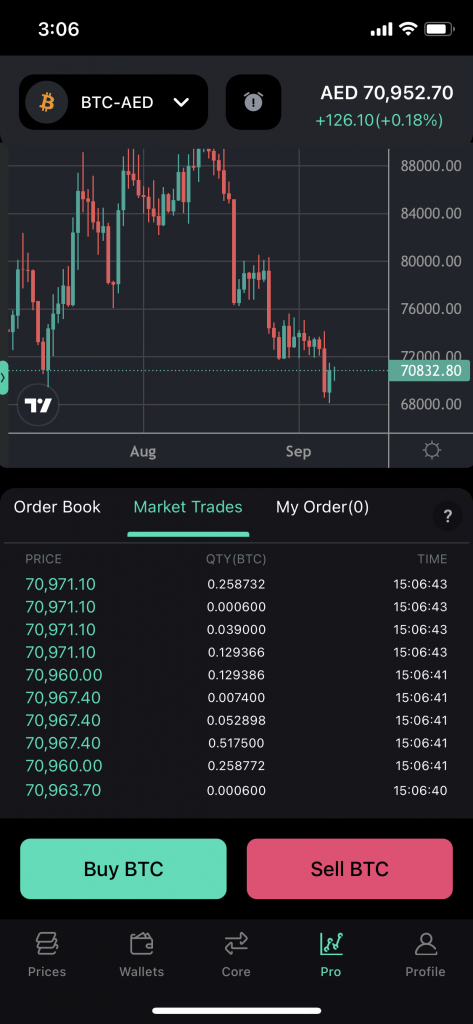
The BitOasis Pro trade history indicates the amount of the digital asset that was traded, the price at which a trade was executed, whether it was a bid or ask (green indicates bid and red indicates ask), and the time each trade was executed for the digital asset you select.
Trading Orders on BitOasis Pro
The types of orders you can execute on BitOasis Pro allow you to indicate whether you are a buyer or seller, what AED or digital asset you want to exchange, how much of the AED or digital asset you want to exchange, and what price you want to exchange it at. You can do this through the following order types:
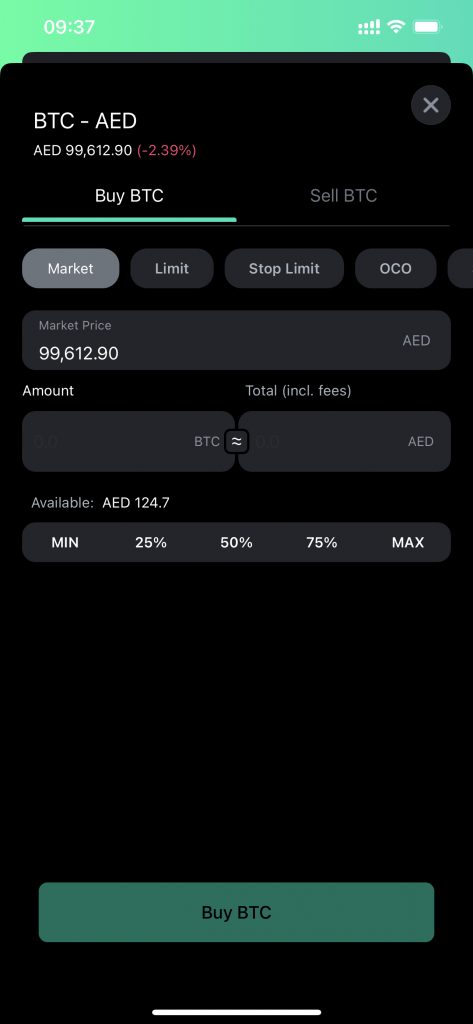
Market Orders
This order type allows you to trade at the market price that is available at the time you are placing the order.
Limit Orders
This order type gives you the flexibility to enter at which price you want your orders to be executed. Your order will be executed automatically only when the market reaches the price you entered.
Fill-or-Kill (FoK) Order:
The Fill-or-Kill (FoK) order allows users to place an order that must be executed in its entirety immediately upon placement, or it will be canceled (“killed”). Unlike other execution types, an FoK order does not allow for partial fills. If the entire order cannot be completed at the limit price at the moment it is placed, the order is canceled.
FoK Order Example:
You want to buy 1,000 XRP at a limit price, say $0.5, using an FoK order. In this scenario, your FoK buy order specifies that you want to buy exactly 1,000 XRP at $0.5, and you want this entire quantity to be filled immediately at this limit price. If there are not enough XRP available at $0.5 to fill your entire order, the order will be canceled, and you won’t buy any XRP. Same logic applied to sell orders.
Immediate-or-Cancel (IoC) Order:
The Immediate-or-Cancel (IoC) order allows users to place an order that must be executed immediately, but any portion of the order that cannot be filled right away is canceled (“immediately or canceled”). Unlike a Fill-or-Kill (FoK) order, which requires the entire order to be filled immediately or canceled, an IoC order allows for partial fills. If only a portion of the order can be filled immediately, the remaining unfilled portion is canceled.
IoC Order Example:
You want to buy 1,000 XRP at a limit price, say $0.5, using an IoC order. In this scenario, you are instructing the market to immediately purchase up to 1,000 XRP at the limit price of $0.5. If there are not enough sellers willing to sell you the full 1,000 XRP at this limit price, the order will be partially filled with as many XRP as are available in the market at that moment, and any remaining unfilled quantity will be canceled. Same logic applied to sell orders.
Note: Since FoK and IoC order execution types immediately take volume off of the order book, a Taker Fee is charged.
Stop Limit Orders (Advanced)
This order type is a combination of a “Stop” order and a “Limit” order. It allows your trade to be executed at a price specified by you. Once the stop price threshold is reached, your Stop Limit order will automatically change to a limit order.
Stop Limit Sell Order Example:
Consider the current price of an asset to be 27,000 AED and you think – based on your analysis – that the market will move to a downward movement once the price reaches 26,000 AED. If this case occurs, you would like to sell your assets at the price of 24,000 AED in order to prevent losses.
The stop (26,000 AED) is the trigger. If you set it lower than the current price (27,000 AED), then when the price of the digital asset reaches that point, it will trigger the limit sell order. The limit field (24,000 AED) is the price of the order that will be placed when the (Stop) is triggered.
Stop Limit Buy Order Example:
Consider the current price of an asset to be 27,000 AED and you think – based on your analysis – that the market will move to an upward movement once the price reaches 28,000 AED. If this case occurs, you would like to buy assets at the price of 28,500 AED to invest or hold.
One-Cancels-the-Other (OCO) Order:
The One-Cancels-the-Other (OCO) Order allows users to place two orders at the same time. Users are able to place a limit order with a stop-market order, and only one of them will be executed. If one order is executed fully or partially, then the other is automatically cancelled.
This option allows you to set both take profit and stop loss targets for your position at the same time while only consuming available balance for one order. The OCO order type simultaneously places a Limit Order and Stop-Market Order. We currently do not support OCO with Limit Order and Stop-Limit Order.
OCO Sell Order Example:
If the market price is 250, and you want a stop sell order at 245 and a limit sell order at 260, then an OCO order may be appropriate. If the market reaches 245, the stop order will trigger a market order and cancel the limit order at 260. If the market reaches 260 before 245, the limit order will execute and cancel the stop order at 245.
Note: If you manually cancel one of the OCO orders, meaning the stop or the limit orders, you can choose to keep the other order open, or you can also manually cancel it.
Stop Order:
A Stop Order is used to trigger a market sell when the market drops to your trigger price or used to trigger a market buy if the market rises to your trigger price.
A Stop order is often used as a stop-loss order if the market is moving in an unfavourable direction. Stop orders will fully execute as a market order once it hits the trigger price.
Stop Sell Order Example:
For instance, if the current market price is 250, the trader is in a long position might want to sell if the price drops to 245 to avoid further losses. A stop sell at 245 can be used in this case.
Stop Buy Order Example:
For example, if the current market price is 250, the trader in a short position might want to buy if the price reaches 255 to avoid further losses. A stop buy order at 255 can be used in this case.
Note: If you want a stop-limit order, and not stop-market order – Please check our Stop Limit order type.
